December 3, 2016: An amazing new robotic telescope feature goes live today! Images of non-special observations are now tweeted and/or emailed immediately after they are taken! The completed queue is still updated in the morning with the raw data.
November 25, 2016: Four new robotic telescope features go live today: three new commands (#domecam, #satellite, and #send) and an improvement to the #weather command. These features mark the first use of in-line images being added with Tweets.
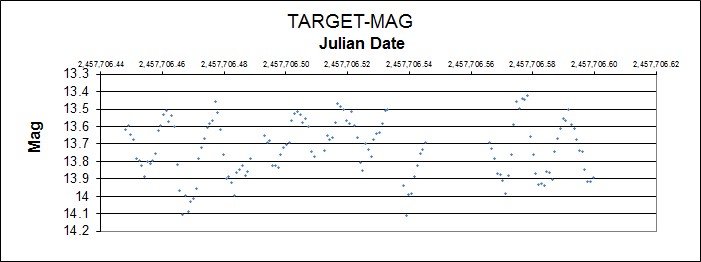
November 14, 2016: Last night I observed (among other things) variable star FO Aqr simultaneously with the x-ray satellite XMM-Newton. The light curve is below which shows time on the horizontal axis (about 3.5 hours) and the star brightness on the vertical axis. It was varying about 0.5 magnitude over a period of about 23 minutes.
October 16, 2016: Two new features go live today - the 'focus' and 'offset' parameters of the #request command.
The 'focus' parameter is intended to be used defocus the telescope when performing photometry of bright stars to reduce overexposure OR to increase photometric precision by blurring stars over more pixels - this can reduce errors caused by how light falls and is recorded by each pixel.
The 'offset' parameter offsets the telescope's position from its catalog position which could be used, for example, to:
- build larger images using a mosaic of separate fields,
- offset a comet's nucleus to a corner of the field so more of the tail can be recorded,
- and place a variable star off-centre so that reference/check stars are in the field of view.
September 30, 2016: A new feature goes live today - the 'epoch' parameter of the #request command. From the documentation:
This advanced parameter is used to precisely constrain when an observation request will start. It is intended to be used to observe during an "interesting" time of a periodically changing object, for example, the eclipse part of an eclipsing binary star's orbit or the transit of an extra-solar planet. It can also be used to constrain the time of night that an observation takes place.
September 29, 2016: This is a couple of months old, but... check out this special issue of Nova Notes (the newsletter of the Halifax RASC) that features 5 articles about using our Twitter-telescope!
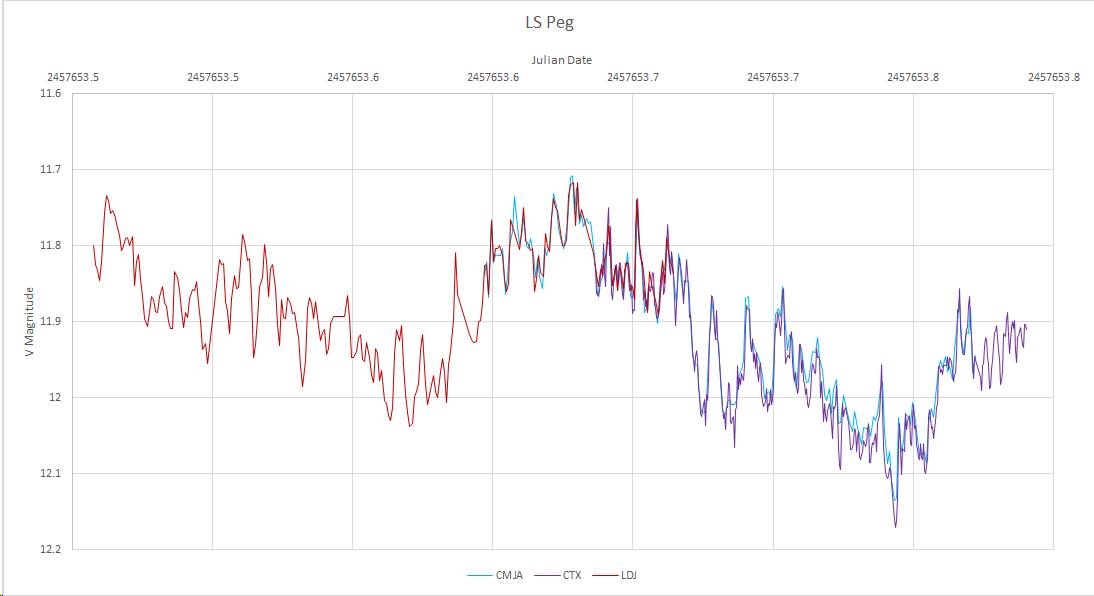
September 22, 2016: Here is an interesting "science" observation taken last night of the star LS Peg (a cataclysmic variable) which ARO observed for 5 hours followed by Newcastle Observatory (Ontario - Michael Cook) and then Tim Crawford (Texas). It shows rapid fluctuations (minute time scale) and a slow ~4 hour cycle which coincides with its rotation period. The power of collaboration!
September 20, 2016: The ARO robot can now be conversed with using Twitter direct messages. You can also now request time series observations and #edit your queued requests!
September 9, 2016: ARO's programs have been updated to BGOs. That means it can be operated now by Twitter DM's too.
May 1, 2016: ARO is now officially online as the world's second Twitter-controlled observatory! I welcome RASC members (and others that I know) to give it a try! It operates identically to the BGO. There are some differences in the available filters and image field of view.
April 30, 2016: A new website is done!
January, 2016: ARO is now the world's second Twitter-operated observatory after the BGO. Documentation on how to use the observatory yourself will be put on-line soon!